【文献名】 Christine E. Kistler, Katharine A. Kirby, et al. Long-term Outcome Following Positive Fecal Occult Blood Test Results in Older Adults. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(15):1344-1351.
【要約】 <Background> In the United States, older adults have low rates (fewer than 60%) of follow-up colonoscopy after a positive fecal occult blood test (FOBT) result. The long-term outcomes of these real world practices and their associated benefits and burdens are unknown.
<Goal> To inform how clinical practice could improve to maximize the net benefit of FOBT screening and follow-up in older adults.
<Methods> Longitudinal cohort study of 212 patients 70 years or older with a positive FOBT result at 4 Veteran Affairs (VA) facilities in 2001 and followed up through 2008. We determined the frequency of downstream outcomes duringthe7years of follow-up, including procedures, colonoscopic findings, outcomes of treatment, complications, and mortality based on chart review and national VA and Medicare data. Net burden or benefit from screening and follow-up was determined according to each patient’s life expectancy. Life expectancy was classified into 3 categories: Best (age, 70-79 years and Charlson-Deyo comorbidity index [CCI], 0), average, and worst (age, 70-84 years and CCI, >=4 or age, >=85 years and CCI, >=1).
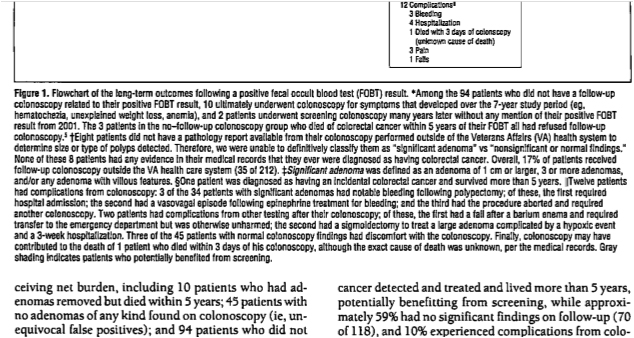
<Results> 56 % of patients received follow-up colonoscopy (118 of 212), which found 34 significant adenomas and 6 cancers. 10% experienced complications from colonoscopy or cancer treatment (12 of 118). 46 % of those without follow-up colonoscopy died of other causes within 5 years of FOBT (43 of 94), while 3% (3 of 94) died of colorectal cancer within 5 years (Figure1). 87% of patients with worst life expectancy experienced a net burden from screening (26 of30) as did 70% with average life expectancy (92 of 131) and 65% with best life expectancy (35 of 51) (P=.048 for trend) (Figure2).
<Conclusions>
Over a 7-year period, older adults with best life expectancy were less likely to experience a net burden from current screening and follow-up practices than are those with worst life expectancy. The net burden could be decreased by better targeting FOBT screening and follow-up to healthy older adults.
Figure1
Figure2
※Charlson-Deyo comorbidity index (Wikipedia) The Charlson co-morbidity index predicts the ten-year mortality for a patient who may have a range of co-morbid conditions such as heart disease, AIDS, or cancer (a total of 22 conditions). Each condition is assigned with a score of 1,2,3 or 6 depending on the risk of dying associated with this condition. Then the scores are summed up and given a total score which predicts mortality. The clinical conditions and scores are as follow: 1 each: Myocardial infarct, congestive heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, dementia, cerebrovascular disease, chronic lung disease, connective tissue disease, ulcer, chronic liver disease. 2 each: Hemiplegia, moderate or severe kidney disease, diabetes, diabetes with complication, tumor, leukemia, lymphoma. 3 each: Moderate or severe liver disease. 6 each: Malignant tumor, metastasis, AIDS. For a physician, it is helpful in knowing how aggressively to treat a condition. For example, a patient may have cancer, but also heart disease and diabetes so severe that the costs and risks of the treatment outweigh the short term benefit from treatment of the cancer. Since patients often do not know how severe their conditions are, originally to calculate the index nurses were supposed to go through the patient’s chart and determine whether the patient had a particular condition. Subsequent studies have adapted it to a questionnaire for patients. The original citation follows: Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR (1987). A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chron Dis, 40(5): 373-383.
【開催日】 2011年10月12日